In the past, the liquid-helium supply and recoverysystem of the Wako campus have suffered severe damages from hydrogen impurities in the system.1) To remove this hydrogen from the recovered helium gas, wedeveloped hydrogen removal methods utilized for oursystem. We found that the Ionex Type Ag400 Zeolite “Ag400” made by “Mingguang Feizhou.” can be used as the adsorbent, and the applicability of Ag400 for hydrogenremoval was confirmed.2) At that time, we did not install the hydrogen removal apparatus earnestly in oursystem. However, a new liquid-helium supply systemwas constructed and operated from 2017 because ofthe deterioration of the old system.3) In this system,the newly established hydrogen removal apparatus wasinstalled beforehand. In this study, we examined theamount of hydrogen that can be adsorbed by Ag400,which had not been minutely evaluated until now.The experimental setup consists of a hydrogen tank,a pressure gauge, a buffer tank, three switch valves, areaction tank, a data logger, and a vacuum pump.
Thevolume of the buffer tank is approximately 550 cc, andthat of the reaction cylinder is approximately 18 cc.These parts are connected as shown in Fig. 1.The experiment is performed by the following threesteps. i) Approximately 20 g of Ag400 Zeolite is filled in thereaction cylinder. Valve 1 is closed and the whole setupare evacuated. ii) Valve 2 is closed, the valve 1 is released and hydrogen gas is filled to the buffer tank;its pressure reaches 0.4 MPaG. iii) Valves 1 and 3 areclosed and valve 2 is released. Hydrogen gas is supplied to the reaction cylinder and adsorption begins.The change of the pressure of the buffer tank is monitored by the pressure gauge and recorded by the datalogger.
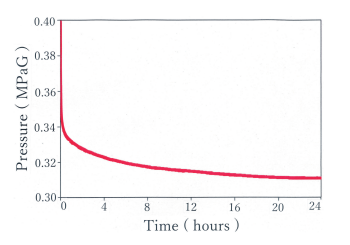
The result of this experiment is shown in Fig. 2.From this figure, it can be observed that the hydrogen pressure in the buffer tank reduced rapidly from0.4 MPaG to 0.34 MPaG in approximately 30 min after the start of the adsorption reaction. After 12 h, thepressure slowly reduced to 0.32 MPaG. Finally, the hydrogen pressure reduced to approximately 0.31 MPaGand settled at the equilibrium state. This result showsthat 20 g of Ag400 can adsorb approximately 500 sccof hydrogen gas throughout the experimental process.We use approximately 4 kg of Ag400 in the hydrogenremoval apparatus in the liquid helium supply and recovery system. Hence, approximately 0.10 Nm3 of hydrogen impurity gas can be removed by this apparatus.Usually, the concentration of hydrogen contained in recovered helium gas ranges from 0.05 ppm to 1.5 ppmin our system. Therefore, supposing that the recoveredhelium gas contains 0.1 ppm of hydrogen, our apparatus can purify approximately 1000,000 Nm3 of recovered helium gas. However, the total volumes of liquidhelium supplied in one year in Wako campus were from180,000 L to 200,000 L.3) When all this liquid helium isvaporized, approximately 135,000 Nm3 to 150,000 Nm3of helium gas is generated. In this case, we will evaluate that 4 kg of Silver Exchanged Zeolite can be used approximately 6–7years for hydrogen removal.In the next steps, we will evaluate other characteristics of hydrogen removal apparatus containing Ag400.
NEWSLETTER SIGNUP
By subscribing to our mailing list you will always be update with the latest news from us.
We never spam!
Copyright © Mingguang Feizhou new materials Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. | Sitemap